Dato' N.Subra Homeopathy
DISEASES OF GLANDS
ASTHMA
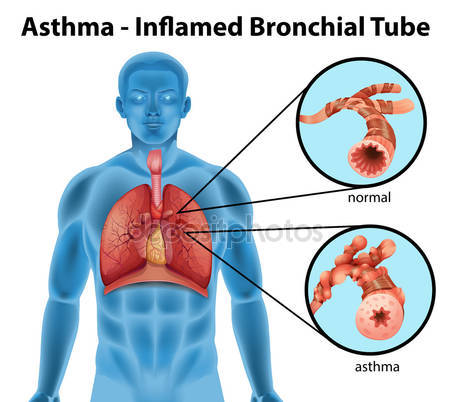
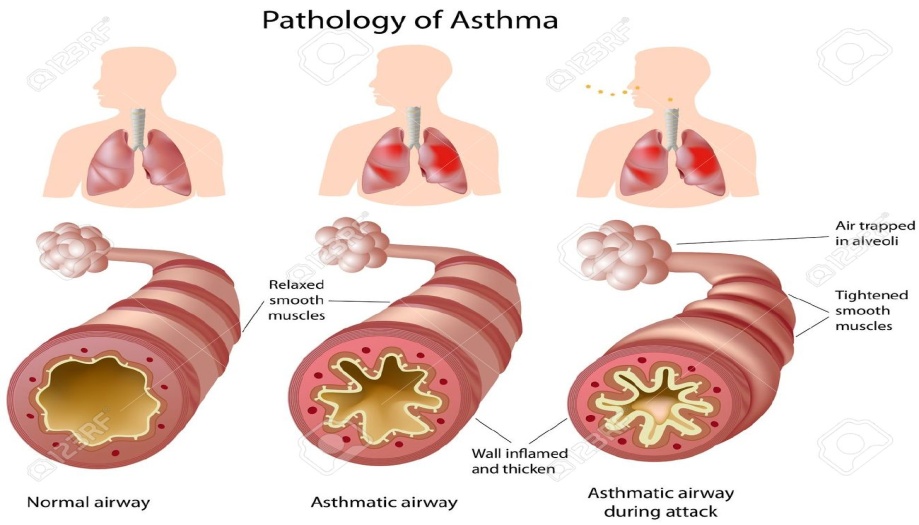
Asthma is an allergic disorder characterised by breathlessness, which is the result of a spasmodic narrowing of the respiratory passages. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs. The lungs get inflamed and the airways become narrow. Breathing becomes difficult or wheezy and a persistent cough develops. Asthma can be triggered by allergies, infections, a grief or the birth of a baby.. Many die from asthma each year. It is a serious disease. The struggle to breathe during an asthma attack can be a frightening experience.
CAUSES
Vaccines, Antibiotic use in early life, Paracetamol use in early life, Family history of asthma
ASTHMA TRIGGERS
Poor or polluted air, Tobacco Smoke, Cold Air,, Emotional Stress Upper respiratory tract infections Exposure to things that provoke an allergic response
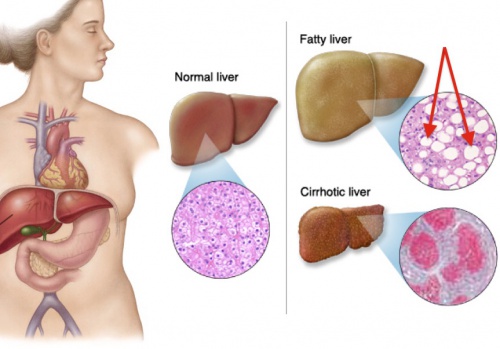
FATTY LIVER
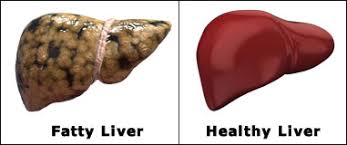

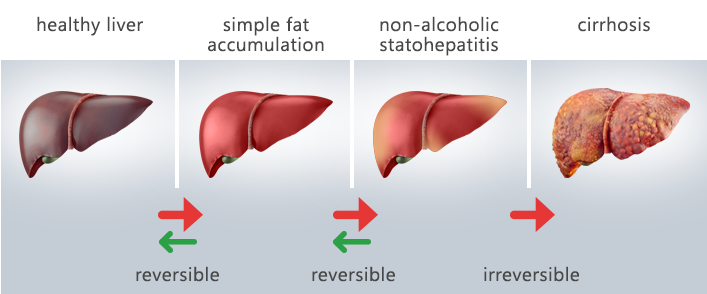
Fatty liver or steatosis, is a term that describes the build-up of fat in the liver. It is normal to have some fat in the liver. If 5 to 10 percent of your liver weight is fat, it can be classified as fatty liver. Fatty liver is a reversible condition that can be resolved with changed behaviours. It often has no symptoms and typically does not cause permanent damage. The liver is the second largest organ in the body. The function of the liver is to process what we eat or drink and to filter harmful substances from the blood. This process is interrupted if too much fat is in the liver. The liver commonly repairs itself by rebuilding new liver cells when the old ones are damaged. When there is repeated damage to the liver, permanent scarring takes place. This is called cirrhosis. Fatty liver is common. Most cases of fatty liver are detected in people between ages 40 and 60. When fatty liver is caused by an underlying condition, it can become harmful to the liver if the cause is not recognized and treated.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF FATTY LIVER
Fatty liver typically has no associated symptoms. Fatigue or vague abdominal discomfort may be felt. The liver will be slightly enlarged and the doctor can detect this during a physical exam. Excess fat can cause liver inflammation. If the liver becomes inflamed, poor appetite, weight loss, abdominal pain, weakness, and confusion show up. smitters.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF FATTY LIVER
The most common cause of fatty liver is alcoholism and heavy drinking. Fatty liver also occurs in people who are not alcoholics. Fatty liver develops when the body creates too much fat or cannot metabolize fat fast enough. The excess fat is stored in liver cells where it accumulates to form fatty liver disease. Eating a high-fat diet may not directly result in fatty liver.
BESIDES ALCOHOLISM, OTHER COMMON CAUSES OF FATTY LIVER INCLUDE:
Obesity, Diabetes, Genetic Inheritance, Rapid Weight Loss Hyperlipidemia or high levels of fats in the blood Certain medication
HOW IS FATTY LIVER TREATED?
There is no medication or surgery to treat fatty liver. The following could assists Managing your cholesterol, Controlling your blood sugar, Losing weight
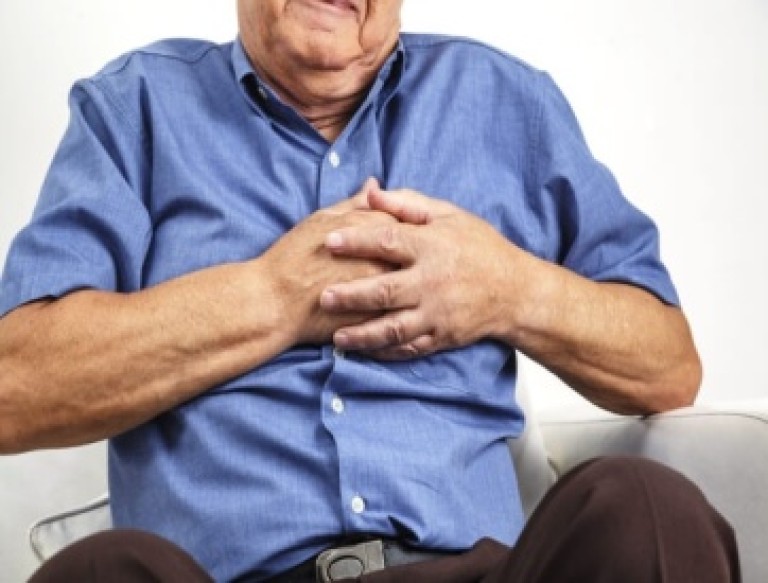
HEART
COMMON HEART CONDITIONS
There are many different heart conditions and problems which are collectively called heart disease. Heart disease and different conditions affect the heart’s ability to work efficiently.
CORONARY HEART DISEASE
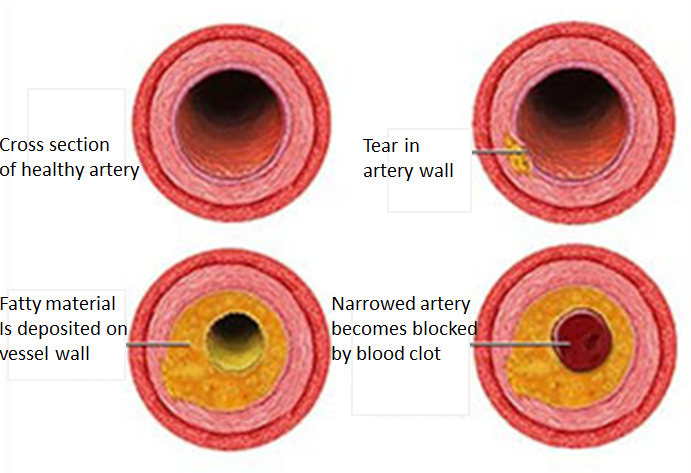
The most common heart condition is coronary heart disease. This is caused when the coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked and thereby blood supply to the heart is limited. This will result in angina or a heart attack
ANGINA
Angina is a pain or discomfort in your chest, arm, neck, stomach or jaw that happens when the blood supply to your heart becomes restricted due to narrowing of the arteries. Angina is a symptom of coronary heart disease. It is not an illness.

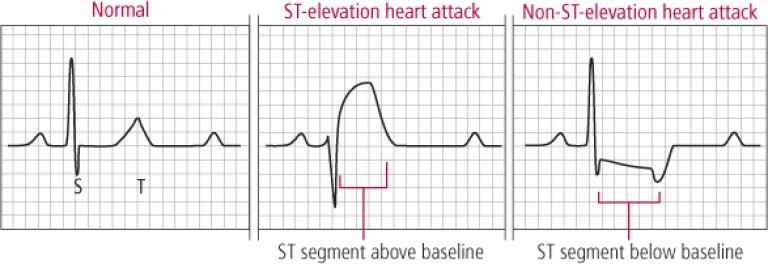
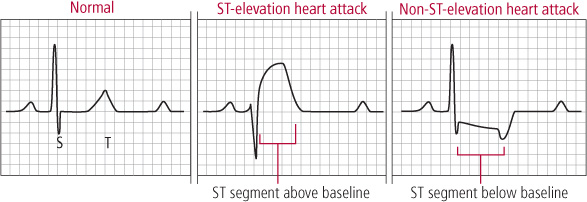
HEART ATTACK
A heart attack, known as myocardial infarction happens when blood supply to a specific heart muscle is completely blocked. This is most commonly caused by a piece of fatty material breaking off and a blood clot forms within a coronary artery. This can cause damage to that part of your heart muscle.
HEART FAILURE
HEART FAILURE The heart is unable to pump effectively therefore there is a decrease supply of oxygen. As a result fatigue and shortness of breath are experienced. This is called heart failure because the heart is unable to function efficiently.
ARRHYTHMIA (ABNORMAL HEART RHYTHMS)
The electrical system of the heart helps to stimulate the heartbeat. If the electrical signals becomes defective, the heart can beat too quickly (tachycardia) or too slowly (bradycardia) or in an irregular way. This is called an arrhythmia.
VALVE DISEASE
The valves open and close to regulate the flow of blood through the heart. Problems with the valves can increase the workload of your heart and can put a strain on your heart muscle.
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
High blood pressure or hypertension can affect the heart. Although it is not a disease, it can lead to coronary heart disease, heart attacks and strokes.
INHERITED HEART CONDITIONS
Inherited condition or genetic heart condition. It can affect any age and can be life-threatening. Death comes suddenly with no obvious cause.
CONGENITAL HEART CONDITIONS
It occurs in developing foetus while in the mother’s womb
KIDNEY STONE, RENAL CALCULUS, RENAL COLIC OR PAIN
Kidney is an extremely complex organ and it eliminates waste from the body. The kidneys conserve proteins, minerals and water. In addition, the kidney also regulates blood pressure. The kidneys are also responsible for ensuring that we maintain appropriate haemoglobin. They produce a hormone called erythroprotein, which stimulates the production of red blood cells
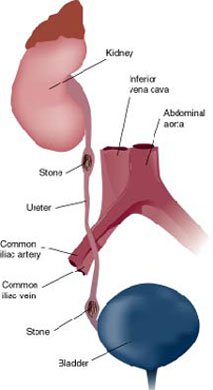
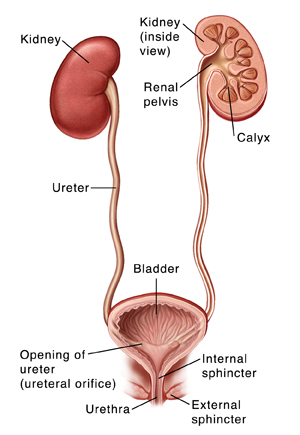
FORMATION OF KIDNEY STONES
The two functions of the kidneys are to conserve water and to eliminate the body’s waste substances. When there is a disharmony or breakdown between these two functions of the kidney, it leads to the formation of stones. Very small stones pass into the ureter and excreted. Large stone remain in the kidney causing mild pain in the loins or an infection may occur. Medium-sized stone enters the ureter and gradually moves down to the bladder causing severe friction and thereby causing pain which is known as renal colic. This pain is wavelike and of a stabbing nature and it starts when the stone moves and stops.
SYMPTOMS OF KIDNEY STONES
The most important symptom of kidney stone is pain. The other symptoms include obstruction in the urinary tract, urinary infection or blood in the urine. These are symptoms cause a lot of suffering and pain. Blood in the urine is not a serious symptom. Once the kidney stones are formed they create an obstruction to the kidney or lead to infection in the body. That is the time when kidney stones begin to damage the kidney. In fact, about 10% to 20% of end-stage kidney disease is because of kidney stones that have been neglected for many years.
TYPES OF KIDNEY STONES
Calcium oxalate stone is the most common stone. The others are magnesium ammonium phosphate stones. Besides these, there could be a uric acid stone that is a component of metabolic disease of the kidney. Mainly calcium oxalate – monohydrate and dehydrate stones are common
GASTRITIS
Gastritis is a general term for a group of conditions with inflammation of the lining of the stomach. Gastritis is most often the result of infection by the bacteria that causes most stomach ulcers. Regular use of certain pain relievers and drinking too much alcohol also can contribute to gastritis. Gastritis can broadly be divided into acute gastritis and chronic gastritis. Acute gastritis occurs suddenly and chronic gastritis appear slowly over time In some cases, gastritis can lead to ulcers and an increased risk of stomach cancer. Most of the time, gastritis is not serious and improves quickly with treatment
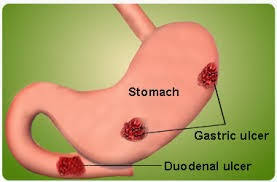
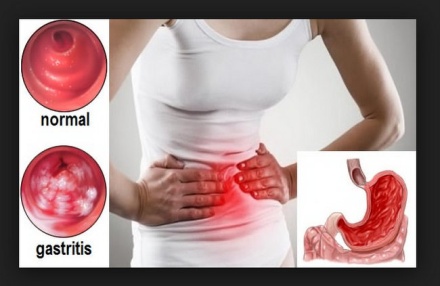
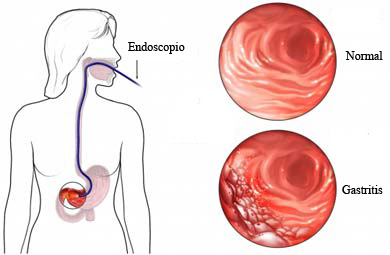
ACUTE GASTRITIS
Acute gastritis is a sudden inflammation of the lining of the stomach. Acute gastritis is a term covering a broad Spectrum of entities which include inflammatory changes in the gastric mucosa.
PANGASTRITIS
Inflammation of the whole stomach
ANTRAL GASTRITIS
Inflammation of part of stomach
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Pain in the upper abdomen, Loss of appetite, Weight Loss Bloating or fullness, Belching, Nausea and vomiting
IN MORE SEVERE CASES
Bleeding inside the stomach, Palpitation and sweating, Short of Breath, Chest and stomach pain, Vomiting large amount of blood, Stool Dark, Sticky and smells
GOITRE
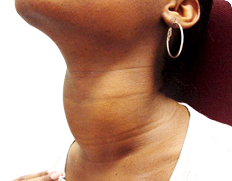
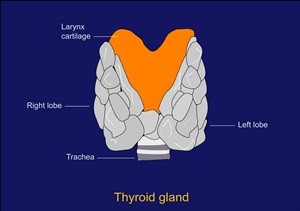
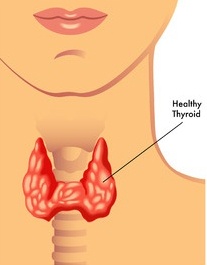
Goitre is an abnormal enlargement of your thyroid gland. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck. Although goitres are painless, a large goitre can cause a cough and make it difficult to swallow or breathe. The most common cause of goitre is a lack of iodine in the diet. The thyroid gland produces two main hormones namely thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).thyroxine
FUNCTIONS OF T3 & T4
T3 and T4 circulate in the bloodstream and help regulate your metabolism. These hormones maintain the rate at which the body uses fats and carbohydrate Help control the body temperature Influence the heart rate Help regulate the production of proteins The thyroid gland also produces calcitonin — a hormone that helps to regulate the amount of calcium in the blood. The pituitary gland and hypothalamus control the rate at which these hormones are produced and released.
CAUSES
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. It is found in seawater and in the soil in coastal areas. Those who live inland or at high elevations are often iodine deficient.
In Graves' disease, antibodies produced by the immune system mistakenly attack the thyroid gland, causing it to produce excess T4. This overstimulation causes the thyroid to swell
It is an autoimmune disorder. Instead of causing the thyroid to produce too much hormone, it damages your thyroid so that it produces too little. Sensing a low hormone level, the pituitary gland produces more TSH to stimulate the thyroid, which then causes the gland to enlarge.
In this condition, several solid or fluid filled lumps called nodules develop on both sides of the thyroid, resulting in overall enlargement of the thyroid
In this case, a single nodule develops in one part of the thyroid gland. The nodules are benign
Thyroid cancer often appears as an enlargement on one side of the thyroid
A hormone produced during pregnancy , human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) may cause the thyroid gland to enlarge
Thyroiditis is an inflammation and can cause pain and swelling of the thyroid. It may cause over production or under production of T4
Visible swelling at the base of the neck, A tight feeling of the throat Coughing & hoarseness, Difficulty swallowing and breathing
SINUSITIS
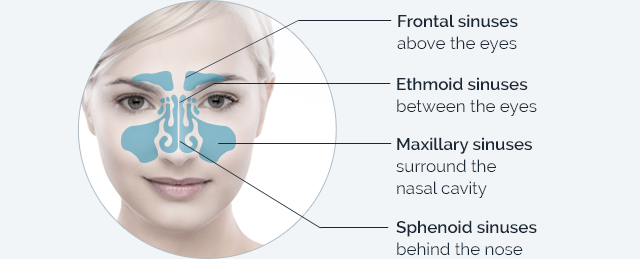
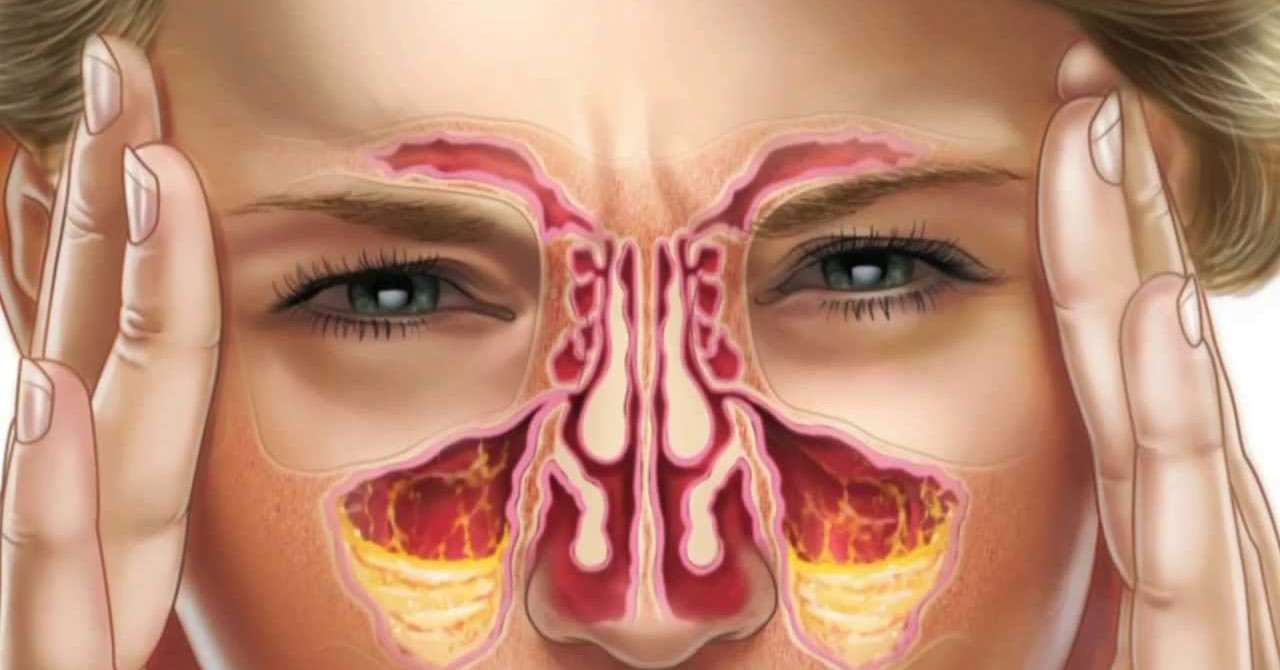
A sinus is a hollow air space in the skull. These are also known as the para-nasal sinuses since they surround the nasal cavity. Sinuses are responsible for exchange of air particles and when they get clogged due to bacterial growth or fluids like mucus it leads to a condition called sinusitis. Inflammation develops on the air cavities of the nose causing sinusitis. Bacterial or fungal infection can cause swelling of sinuses. Sinusitis can cause symptoms like headache, fever, sore throat, stuffiness in the nose and nasal discharge. Sinusitis is usually caused by a virus and often persists even after other upper respiratory symptoms disappear. Fungus or bacteria may cause a sinus infection. Allergies, nasal polyps, a tooth infection, and a deviated septum can also trigger sinusitis
COMMON CAUSES OF SINUSITIS
Viruses, bacteria or fungus, Excessive nose blowing Foreign objects in nostril (especially in children) Scuba diving, Side effects of certain drugs, Tooth caries and Allergies
COMMON SYMPTOMS
Nasal congestion and discharge that may be yellowish or greenish Cough with production of mucus Discharge from the back of the nose into the throat Bad breath, Headache and Toothache Reduced sense of smell/ taste Pain in the region of the affected sinus Fever, Tiredness and Weakness
Dato' N.Subra Homeopathy
The Homeopathy