
Dato' N.Subra Homeopathy
WOMEN’S DISEASES
ANAEMIA
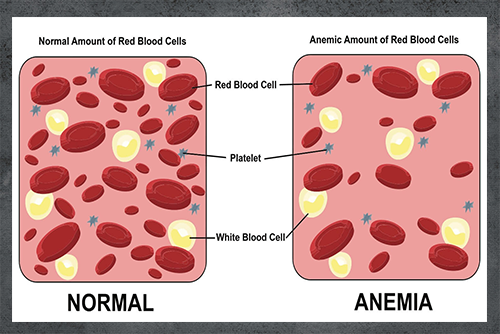
Anaemia is the condition where either the absolute number of the red blood cells is low or the haemoglobin level in an individual RBC is low. The normal level of haemoglobin in men is about 14 -16 gm/100ml while in a female; it is 12-14 gm/100ml.
If you are anaemic, you will suffer from short of breath very easily. This is mainly because of the decreased ability to transport oxygen in the blood. The heartbeat tends to increase disproportionately while exercising or climbing stairs. The eyes and the skin of the face, hands, and feet will be pale.
VAGINAL INFECTION
MOST COMMON VAGINAL INFECTIONS
CANDIDA OR YEAST INFECTION
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS
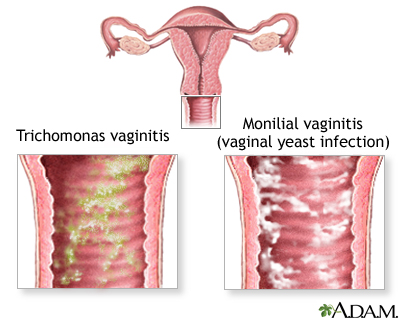
TRICHOMONIASIS VAGINITIS
VIRAL VAGINITIS
FEMALE BREASTS
Breasts are the attractive part of females. Some females get depressed and frustrated due to small breasts while some are unhappy with very large breasts. Some feel depressed because of defective shape or size. Oestrogen, the female sex hormone promotes breast development at puberty.
The female breasts develop various types of disorders. Do not conclude that all changes or lumps in the breast tissues are cancerous. If you find an abnormality or notice any changes, you should talk to us or your doctor. Some of the commonly occurring types of breast disorders are illustrated in the drawing below.
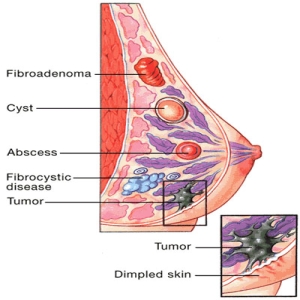
FIBROADENOMAS
They are non-cancerous growths in the breast tissue. These growths are painless lumps and are not attached to any structures in the breast. A fibro adenoma can be removed surgically but homeopathy treats it with medication.
CYSTS
They are fluid-filled sacs. The cause is unknown. Most often, cysts are not harmful. They may sometimes cause pain. Your doctor may draw out the fluid with a needle. Do you know homeopathy treatment can solve your problems with medication?
A TUMOUR
In cases where the tumour is cancerous, it may appear as a white area on a mammogram. A cancerous tumour may have no symptoms A breast biopsy is helpful in determining whether a mass is cancerous.
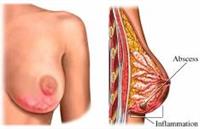
BREAST ABSCESS
A BREAST ABSCESS is a collection of pus, due to an infection. Symptoms include tenderness and inflammation.
FIBROCYSTIC BREAST DISEASE
It is a common condition characterized by an increase in the fibrous and glandular tissues in the breasts. Small, nodular cysts, non-cancerous lumps and tenderness exist.
CONCLUSION
If you have any of the above, please DO NOT act in haste. Contact us and we will help you to solve your problems in the best manner we could think of without going for surgery.
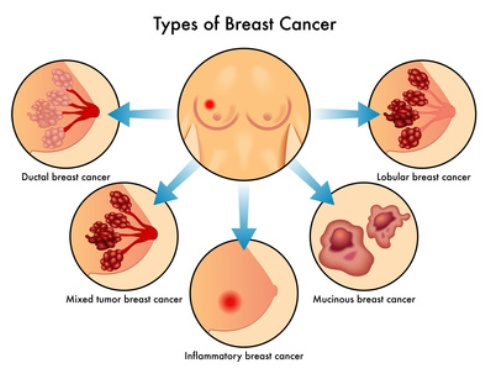
A cancerous tumour in the breast is a mass of breast tissue that is growing in an abnormal, uncontrolled way. The tumour may invade surrounding tissue or shed cells into the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Invasive breast cancer is one of the most dangerous diseases. Most breast cancer patients are women.
SYMPTOMS OF BREAST CANCER
BREAST SWELLING, SUDDENLY ONE BREAST IS LARGER THAN THE OTHER
BREAST THAT FEELS WARM TO TOUCH AND MAY LOOK INFECTED
ITCHING OR SHOOTING PAIN
A DIMPLING OF THE BREAST SKIN THAT LOOKS LIKE AN ORANGE PEEL THICKENING OF THE SKIN
FLATTENED OR DISCOLORED NIPPLE
SWELLING IN UNDERARM OR ONLY ON ONE SIDE OF NECK
FEELS A LUMP, HOWEVER LUMPS ARE NOT COMMON IN IBC.
ENDOMETRIOSIS AND ADENOMYOSIS
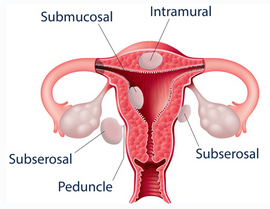
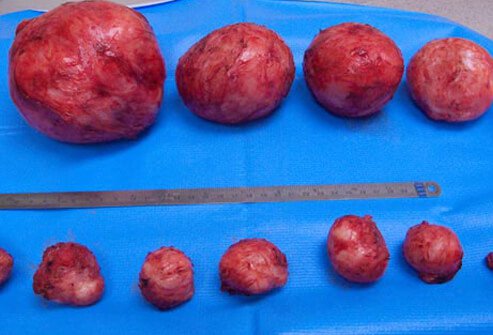
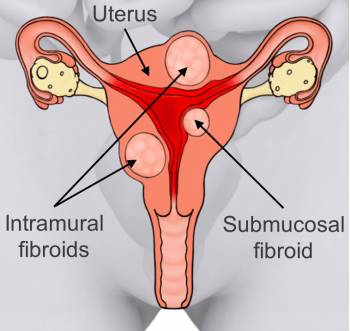
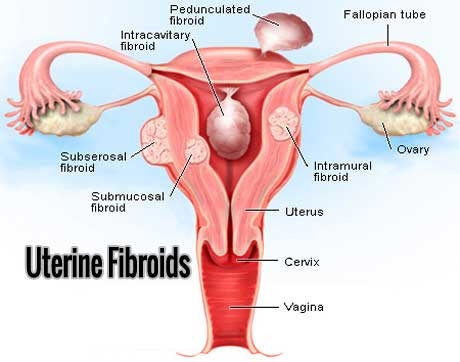
Fibroid tumours are benign smooth muscle tumours present in the uterus. They are made up of muscle cells of the uterus. The size of fibroids varies in size. They may be like a small seed. In some cases they may become quite large and take up almost complete wall of the uterus. In extreme cases large uterine fibroids have been known to push the uterus up till the rib cage. Usually large fibroids push against the urinary bladder. The chances of developing a cancerous growth do not increase because you have uterine fibroids, nor does having them increase your chances of getting other uterine cancers. Most of the women would not know that they have uterine fibroids because there will not be any visible symptoms.
COMMON SYMPTOMS
The most common symptom is a change in the normal menstrual bleeding pattern
Abnormal bleeding during menses
Pain during intercourse
Infertility and Anaemia
Fullness in the lower abdomen
Pain during menses. Pain may be felt in the lower back, lower abdomen and pelvis
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME (PCOS)
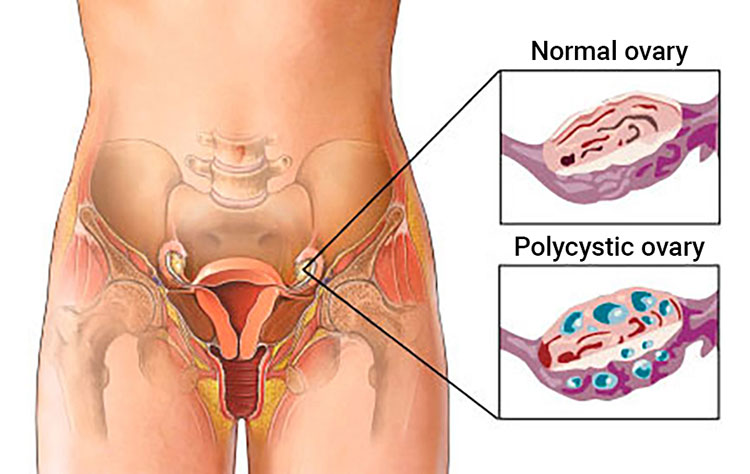
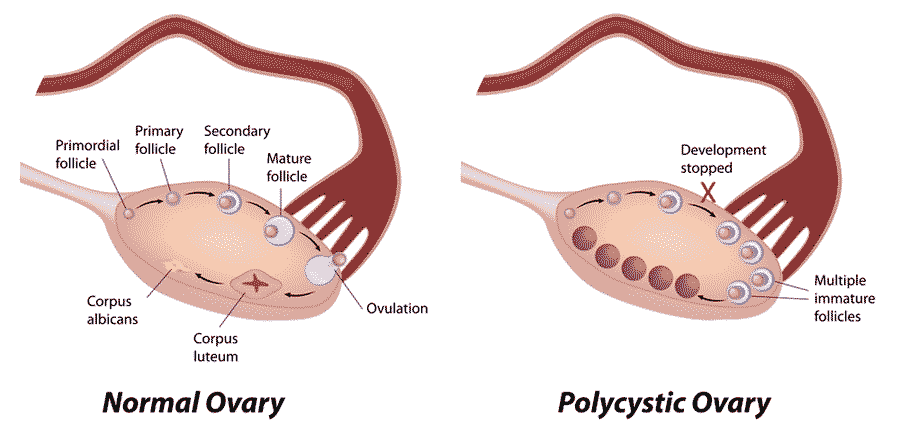
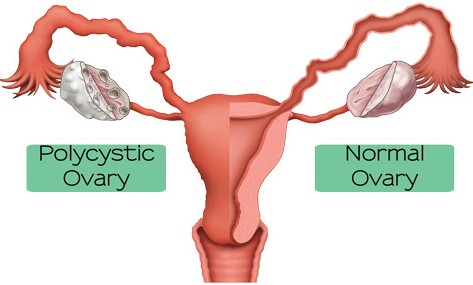
PCOS is a problem in which a woman's hormones are out of balance. It can cause problems with your periods and make it difficult to get pregnant. PCOS also may cause unwanted changes in the way you look. If it is not treated, over time it can lead to serious health problems like diabetes and heart disease. Most women with PCOS grow many small cysts on their ovaries. That is why it is called polycystic ovary syndrome. The cysts are not harmful but lead to hormone imbalances. The adrenal glands and ovaries produce excessive amounts of male hormone, which leads to an abnormally high production of luteinizing hormone (LH) and an abnormally low production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). As a result, the ovary fills with cysts of immature follicles that are unable to generate eggs. Early diagnosis and treatment can help control the symptoms and prevent long-term problems.
SYMPTOMS OF POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME (PCOS)
Irregular or absence of menses
Enlarged ovaries
Excessive facial and body hair,
Oily skin, Acne
Obesity
Hair loss
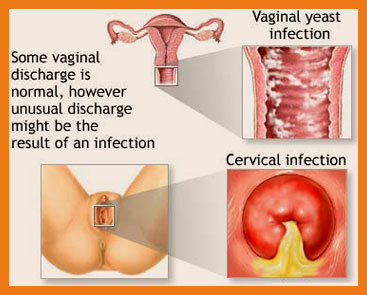
TYPES OF LEUCORRHEA
PSYCHOLOGICAL LEUCORRHEA
It is an excessive discharge or secretions of a normal vagina. They are slimy in nature and generally occur among teenage girls due to hormonal imbalance during puberty, at the time of ovulation period of the menstrual cycle or before periods.,
In case of adults, in addition to the ovulation time and before periods, it occurs also during early days of pregnancy and during sexual excitement. Generally, no medication is required in this kind of discharge.
PATHOLOGICAL LEUCORRHEA
It is a discharge occurring due to disease or malfunction of the female reproductive tract. It needs immediate attention, cleanliness and treatment. Ignoring pathological leucorrhea may lead to serious problems like loss of fertility or even removal of uterus. The nature of discharge varies from slimy to thick bloody discharge with foul smell.
CAUSES OF LEUCORRHEA
Synthetic undergarments and poor hygiene conditions.
PARASITE
Sexual Intercourse and moist clothes.
BACTERIA
Venereal Diseases.
IRREGULAR MENSES OLIGOMENHRREA

An irregular period, medically known as oligomenorrhea, is a common problem among women. It usually refers to infrequent periods with intervals of more than 35 days. A normal menstrual cycle ranges from 21 to 35 days. Menstrual bleeding generally lasts for two to seven days. Women normally have 11 to 13 periods in a year, but those with oligomenorrhea may have fewer than six or seven periods.
THE CAUSES OF IRREGULAR MENSES
The menstrual cycle functions with the rise and fall of hormones oestrogen and progesterone. An imbalance in these hormones results in delayed menses. ,br/> Delayed menses also occur due to lack of ovulation. Pregnancy and hormonal pills such as oral contraceptives often also cause menstrual delay. ,br/> Delayed menses are also associated with other hormonal diseases such as polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD), emotional stress and grief. Thyroid disease, Stress, travelling overseas, polycystic ovarian syndrome, early menopause or premature ovarian failure, uterine fibroids and polyps, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), Endometriosis, Gaining or losing weight, Too much exercise, Birth control pills, Other medications.


Bleeding through the vagina that occurs any time in between the expected date of hormonal cycle is known as the Inter Menstrual Bleeding or Metrorrhagia.
CAUSES
MENTAL Emotional, Excitement, Anger, Fright
PHYSICAL Injury or Exertion
PHYSIOLOGICAL Fibroids, Polyps in uterus, Endometriosis, Adenomyosis, Uterine Fibroids and Malignancies
MENOPAUSE
The menopause is the change of life that signals the end of your childbearing years. It generally occurs between the ages of 45 and 55 years but can start before or after this for a variety of reasons.
Age is the leading cause of menopause. Certain surgeries and medical treatment can induce menopause. Those include surgical removal of the ovaries, chemotherapy and pelvic radiation therapy. Having a hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) without removing the ovaries does not lead to menopause, although you will not have periods anymore.

WHAT HAPPENS AT MENOPAUSE?
The release of eggs from the ovaries becomes more erratic and your monthly periods space apart and eventually stop. As oestrogen levels fall, many women experience symptoms like hot flushes, night sweats, headaches, emotional moods and falling libido.
Your natural hormone balance is a finely-tuned rhythm of oestrogen and progesterone. As one hormone increases, another subsides as they all have a different job to do in reproductive processes. At the menopause, oestrogen and progesterone levels fall. Many women sail through the menopause symptom-free, whilst others experience troublesome symptoms for months and even years.
ARE MENOPAUSAL SYMPTOMS TREATABLE?
The conventional view of the menopause is that it is a disease that needs to be treated. By replacing the ‘lost’ hormones, using Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) in the form of pills, patches or creams, the medical profession believes it offers one simple answer to the problems women face. But natural methods are available too, including homeopathy.
If we were to view the menopause as a ‘deficiency disease’, a logical solution would be to replace the missing hormones with artificial ones by giving HR, but we now know this is not a risk-free option. Artificially replacing oestrogen and progesterone in a constant dose is like driving a car in one gear; you may have more energy but there are serious long-term implications for our health.
New clinical guidance recommends GPs offer HRT in only the worst cases and for a period of only five years. Both the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists and the British Medical Association discourage GPs from prescribing HRT to prevent osteoporosis. “HRT is no longer considered a safe option for women.”
RESEARCH FINDINGS
A significant risk of breast cancer was demonstrated by those taking combined HRT (estrogen and progesterone). The researchers estimate there have been 20,000 cases of breast cancer over the last decade owing to HRT. It was also found that estrogen-only HRT carries a significant risk of endometrial cancer.
The results of another large trial of 16,000 women studied in Houston, Texas, found they did not gain any symptomatic improvement from menopausal symptoms such as hot flushes nor from emotional symptoms such as mood-swings after using HRT. In earlier studies HRT has also been linked to stroke and its role in protecting against osteoporosis has not been borne out by other trials.
HOMEOPATHY IS AN ALTERNATIVE TO HRT
Homeopathy is safe and effective, especially when used in conjunction with lifestyle and dietary changes, in the treatment of hot flushes, mood-swings, menopausal headaches and a host of other troublesome symptoms. Evidence has shown the benefit of homeopathy in this area and a NHS Well-Woman clinic in Sheffield offering homeopathic treatment to these women is now in its seventh year and is an established service.
DIET & EXERCISE
At the menopause, it is important to make other changes to your life. Changes to your diet, such as increasing foods that contain natural phyto-estrogens (soya products are rich in these) and reducing protein in your diet, may check osteoporosis. By taking Vitamin E and avoiding hot spicy food, you may reduce hot flushes and by drinking fewer caffeine-rich drinks, you can reduce anxiety and palpitations.
Weight-bearing exercise, such as walking or jogging, is great for maintaining the health of your bones and swimming and yoga will maintain joint mobility. Your homeopath may offer advice on diet and exercise.
INFERTILITY
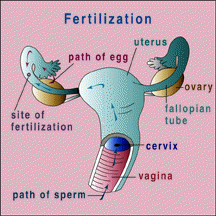
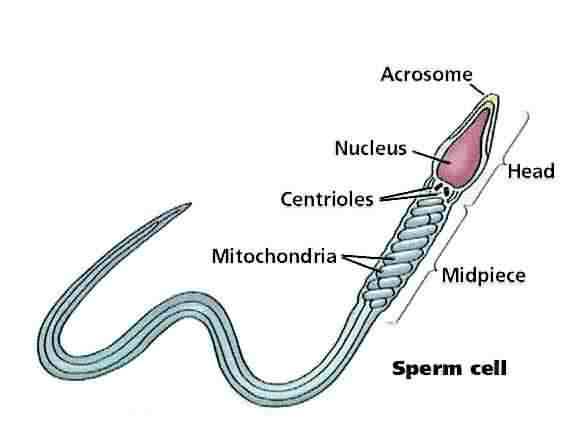
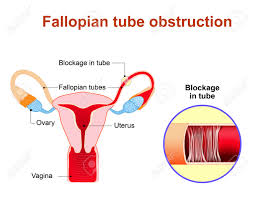
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive despite having regular unprotected sex for one or more than one year The cause for infertility can be either present in the male or female
CAUSES OF INFERTILITY IN MALES
CAUSES OF INFERTILITY IN FEMALES
COMBINED CAUSES OR RISK FACTORS IN MALE/FEMALE THAT INCREASE THE RISK OF INFERTILITY
Advancing age, obesity, alcohol intake, smoking, diabetes mellitus, emotional stress, exposure to radiation and intake of certain drugs are the primary causes for this condition.
HORMONAL IMBALANCE


HORMONAL CHANGES CAN AFFECT ANYONE
SYMPTOMS
PERSISTENT WEIGHT GAIN
Many women have underlying hormonal imbalances that make it difficult to maintain a healthy weight
BELLY FAT AND LOSS OF MUSCLE MASS
When the endocrine system is under stress there is an underproduction of certain hormones and an overproduction of others (mainly cortisol). This makes your body store fat for future use, making an increase in belly fat a clue to adrenal fatigue
LOW LIBIDO
One of the most noticeable symptoms of hormonal imbalance is low libido, which starts with disturbed sleep. Without quality sleep sex hormone production can diminish.
FATIGUE
Feel sluggish, scattered or mentally foggy. Anxiety, irritability and depression
INSOMNIA AND POOR SLEEP PATTERNS
Starts with physical stress and increase in cortisol levels, which directly causes many hormonal imbalances. Night sweats and hot flashes
DIGESTION PROBLEMS
Gas, bloating, slow digestion and craving. Common causes of cravings and excess eating are adrenal fatigue, insulin resistance, and other hormonal imbalances.
HORMONE IMBALANCE IN MALES
Hormone imbalance mainly testosterone in males results in major complaints of erectile dysfunction, infertility, low sex drive, breast development depression, loss of muscle strength, decreased bone density, falling of hair and lowered energy levels.
HORMONE IMBALANCE DUE THYROID GLAND DYSFUNCTION
Thyroid gland mainly controls the metabolic functions of the body. Hormones produced by the thyroid gland are TSH, T3 and T4. Imbalance of these hormones results in either of the two conditions – hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (hyperactive thyroid).
HYPOTHYROIDISM MAINLY RESULTS IN SLOWING OF
ALL BODILY METABOLIC FUNCTIONS.
SYMPTOMS
WEIGHT GAIN, CHILLY FEELING, CONSTIPATION, HAVY PERIODS AMONG WOMEN, FEELING OF FATIGUE AND SLOWNESS/SLUGGISHNESS.
HYPERTHYROIDISM, THE METABOLIC FUNCTIONS ARE ACCELERATED.
SYMPTOMS
HEATED FEELING, WEIGHT LOSS, HAND TREMORS, RESTLESSNESS, IRRITABLE MOOD, TIREDNESS, PALPITATIONS AND
SHORTNESS OF BREATH, DIARRHOEA, AND SCANTY PERIODS IN WOMEN AND PROTRUDING EYEBALLS.
BREAST FEEDING
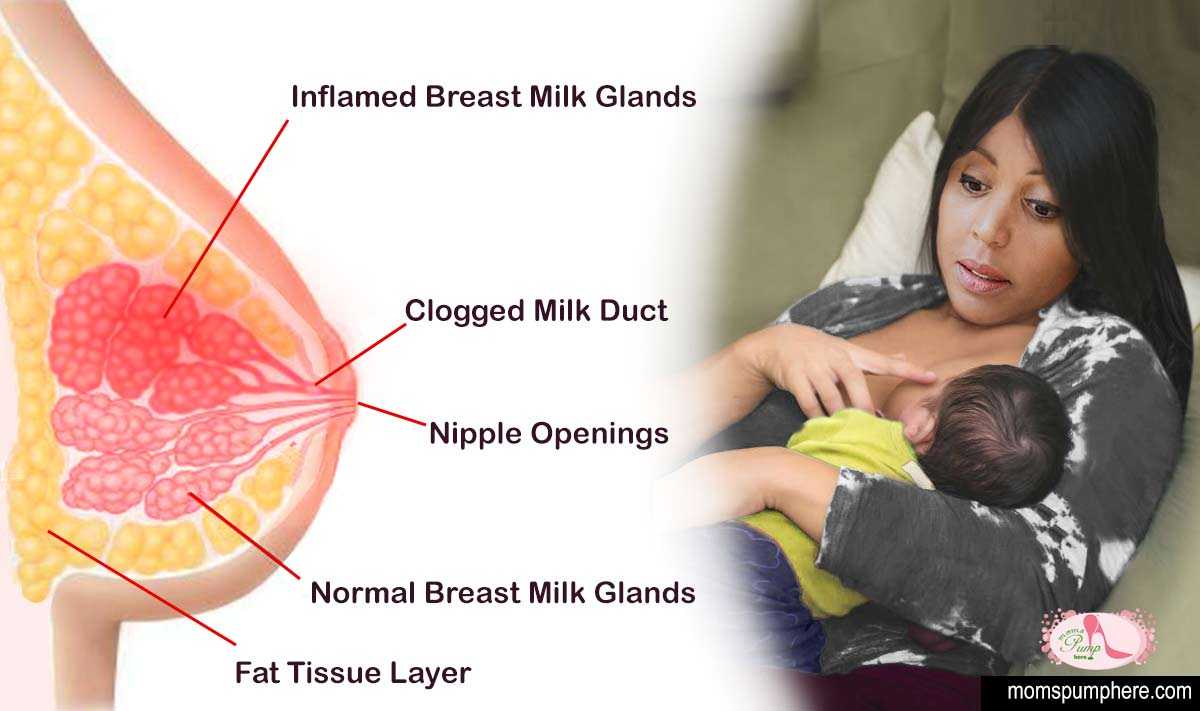
Research findings reported that 85% women with newborn babies breastfeed them and the percentage is growing. It was found that breastfeeding improves the immune function in babies. The findings indicated that babies who drank formula milk are more prone to ear infections, diarrhoea in the first six months and face a higher lifetime risk of asthma, obesity, type 2 diabetes and other health problems.
CHALLENGES FACED BY BREATFEEDING WOMEN
NIPPLE PAIN OR CRACKING
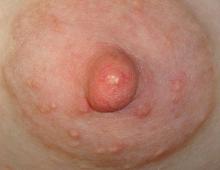
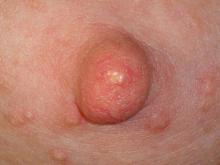
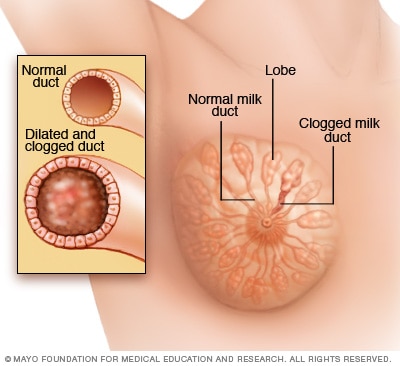

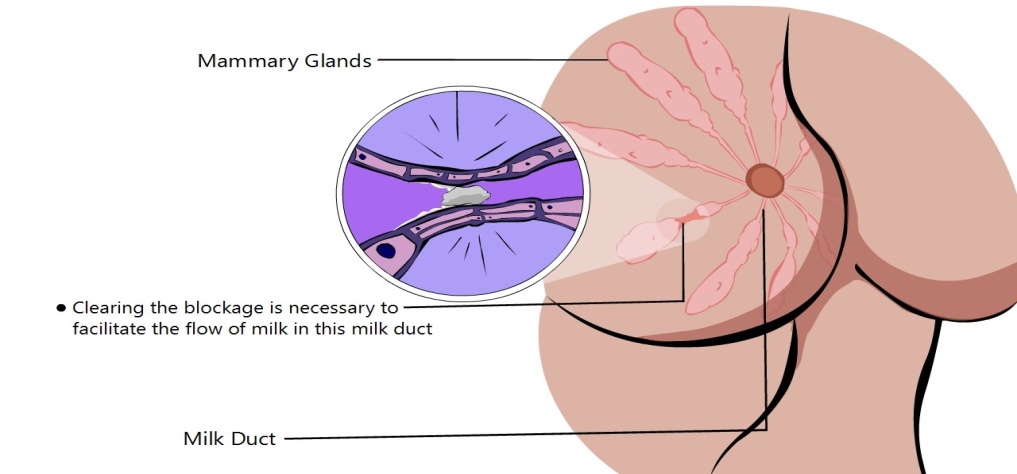
MASTITIS
Mastitis is inflammation of the breast usually caused by a blockage. It could be due to bacterial or fungal infection. Mastitis usually occurs in breastfeeding mothers. In these instances, the breast milk being produced behind a blockage seeps into the surrounding tissue which then causes an inflammatory response. However, mastitis can occur even in women who are not breastfeeding or pregnant and can even occur in small babies.
Nobody knows exactly why some women get mastitis. Bacteria may gain access to the breast through a crack or sore in the nipple, but women without sore nipples also get mastitis. Mastitis needs to be differentiated from a blocked or plugged milk duct. A blocked duct does not need to be treated with antibiotics, whereas mastitis often requires treatment with antibiotics.
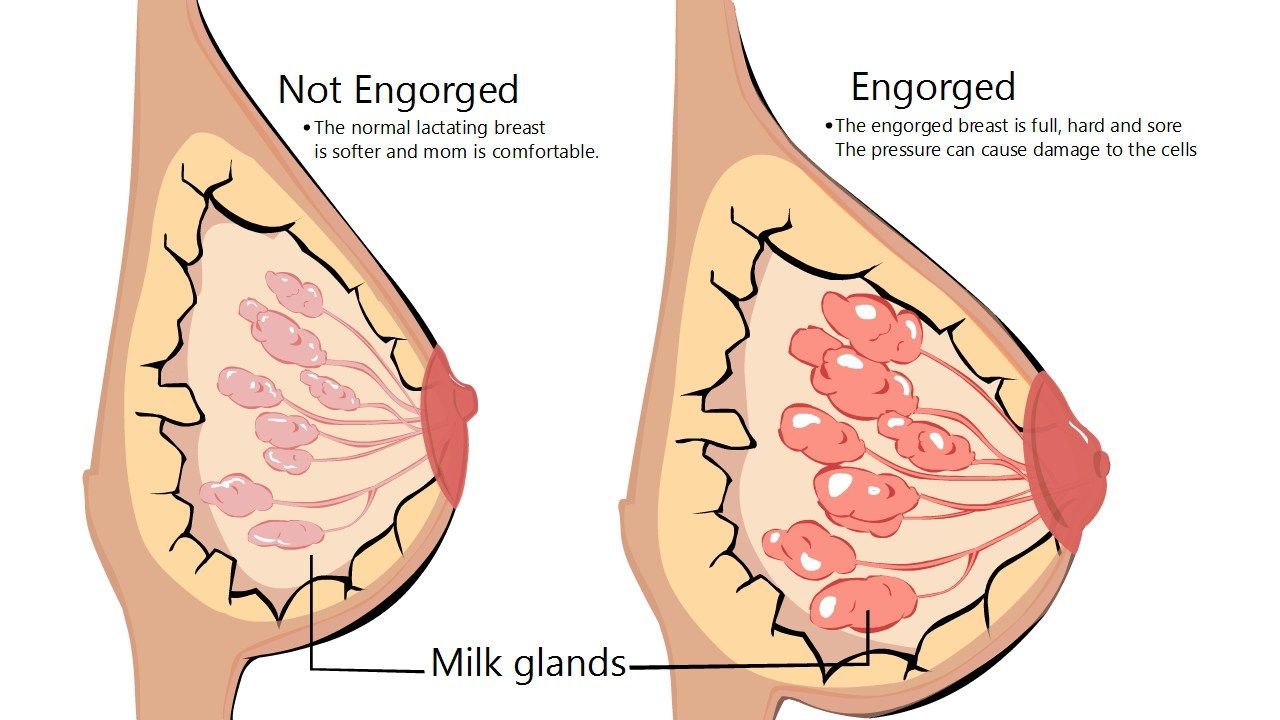
INADEQUATE OR EXCESSIVE
SUPPLY OFMILK
The challenges can be frustrating and even result in discontinuing breastfeeding. Homeopathy remedies help women overcome the challenges make breast feeding experience more enjoyable. Last but not least, homeopathy remedies are safe as they are free of chemicals.
BEFORE TREATMENT IS ADMINISTERED Examine the breasts to see if there is any discolouration or swelling Check the nipples to see any irregularities Check the texture and appearance of the milk Find out if the baby has any problems related to feeding
Dato' N.Subra Homeopathy
The Homeopathy