
Dato' N.Subra Homeopathy
PROBLEMS IN ABDOMEN
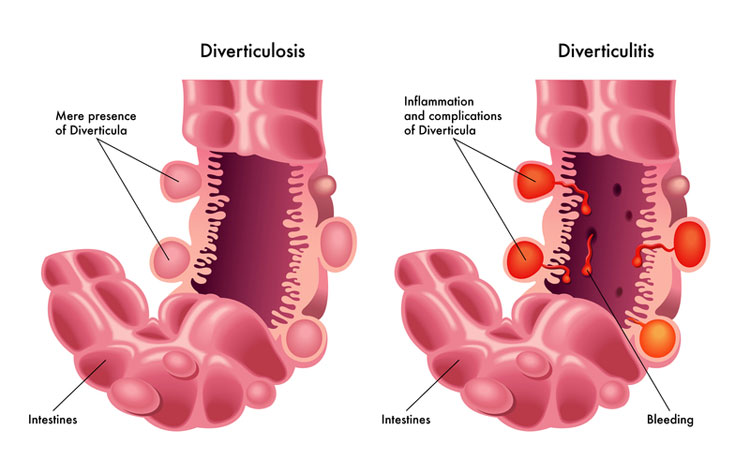
DIVERTICULITIS
Diverticulitis is a common condition that affects half of the population over the age of 60. This disease is characterised by one or several areas of bulging sacs or diverticula, in the inner lining of the intestine. A bowel affected with diverticula may trap faeces, grow bacteria and become inflamed. Infected and painful diverticula are known as diverticular disease or diverticulitis. Diverticulitis is a painful condition in which a small pouch or sac in the wall of the digestive tract become inflamed or infected. Mostly these pouches are found in large intestine. It is more common in the lower portion of the large intestine, called sigmoid colon. It is presented as abdominal pain with cramping, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills or changes in the bowel habits. Mild cases of diverticulitis can be treated with rest, dietary changes and antibiotics but serious cases of diverticulitis may be requiring surgery.
CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS
EXACT CAUSE NOT KNOWN. EXPERTS AGREE THAT A DIET LOW IN FIBRE IS A CONTRIBUTING FACTOR. A DIET LOW IN FIBRE CAN CAUSE CONSTIPATION AND THIS INCREASES STRAINING DURING BOWEL MOVEMENT. THE PRESSURE EXERTED BY THE FORCE OF THE FAECES CAUSES THE POCKETS TO STRETCH AND BULGE. WASTE MATERIALS BECOMES TRAPPED IN THE POUCHES AND CAUSE INFECTION, PAIN AND EVENTUALLY RUPTURE CAUSING FATAL, SEPTIC CONDITIONS
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Moderate to severe pain usually begins in the lower left side of the abdomen. Pain increases with movement or applied pressure. Cramping in the lower abdomen with excessive gas and bloating. If infected experience fever and chills. In addition, there can be nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and loss of appetite. Abnormal levels of brain chemicals called neurotransmitters.
TYPES OF ABDOMINAL PROBLEMS
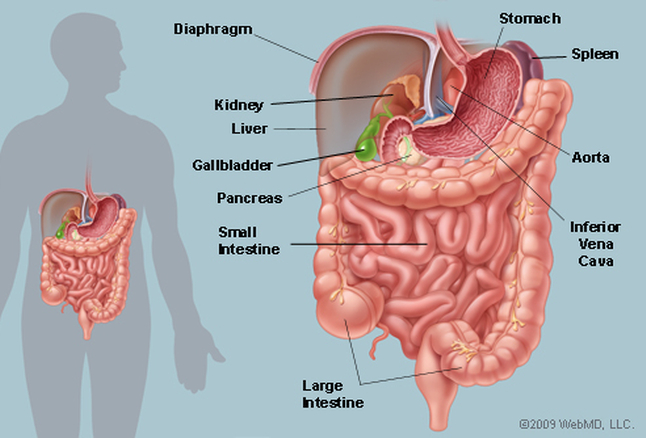
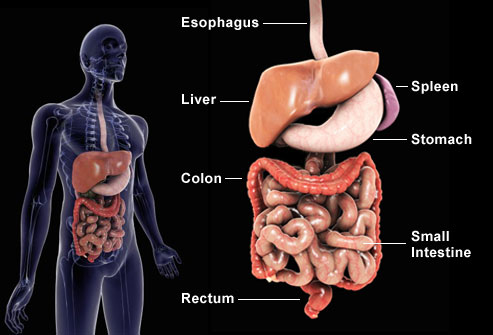
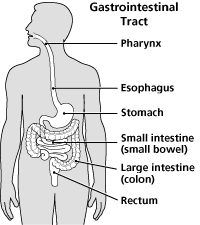
The abdomen is the body space between the thorax and pelvis. The diaphragm forms the upper surface of the abdomen and the pelvis lower.
The abdomen contains all the digestive organs, including the stomach, small and large intestines, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. These organs are held together loosely by connecting tissues (mesentery) that allow them to expand and to slide against each other. The abdomen also contains the kidneys and spleen.
Many important blood vessels travel through the abdomen, including the aorta, inferior vena cava, and dozens of their smaller branches. In the front, the abdomen is protected by a thin, tough layer of tissue called fascia. In front of the fascia are the abdominal muscles and skin. In the rear of the abdomen are the back muscles and spine.
TYPES
PERITONITIS
It is an inflammation of the covering of the abdominal structures, causing rigidity and severe pain. Usually, this is due to a ruptured or infected abdominal organ.
ACUTE ABDOMEN
A medical phrase doctors use to suggest that peritonitis or some other emergency is present and surgery is likely needed.
APPENDICITIS
It is the inflammation of the appendix, in the lower right colon. Usually, an inflamed appendix must be removed by surgery.
CHOLECYSTITIS:
It is an inflammation of the gallbladder, causing severe right-sided abdominal pain. A gallstone blocking the duct exiting the gallbladder is usually responsible.
DYSPEPSIA
It is the feeling of an upset stomach or indigestion. Dyspepsia can result from benign or more serious conditions.
CONSTIPATION
It is having fewer than three bowel movements per week. Diet and exercise may help but many people will need to see their health care providers.
GASTRITIS
It is an inflammation of the stomach, often causing nausea and/or pain. Gastritis can be caused by alcohol, NSAIDs, H. pylori infection, or other factors.
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE:
Ulcers are erosions and peptic refers to acid. Peptic ulcers are ulcers in the stomach and duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). The usual cause is either an infection with H. pylori or taking anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen.
INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION
A single area of the small or large intestine can become blocked or the entire intestine may stop working. Vomiting and abdominal distension are symptoms.
GASTROPARESIS
The stomach empties slowly due to nerve damage from diabetes or other conditions. Nausea and vomiting are symptoms.
PANCREATITIS
It is the inflammation of the pancreas. Alcohol and gallstones are the most common causes of pancreatitis. Other causes include drugs and trauma; about 10% to 15% of cases are from unknown causes.
HEPATITIS
It is an inflammation of the liver, usually due to viral infection. Drugs, alcohol, or immune system problems can also cause hepatitis.
CIRRHOSIS
It is scarring of the liver caused by chronic inflammation. Heavy drinking or chronic hepatitis is the most common cause.
ASCITES
Abdominal fluid build-up often caused by cirrhosis. It cause the abdomen to protrude impressively.
ABDOMINAL HERNIA
A weakening or gap in the abdominal fascia allows a section of the intestine to protrude.
ABDOMINAL DISTENSION:
It is the swelling of the abdomen, usually due to an increased amount of intestinal gas.
ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM
A weakening of the aorta's wall creates a balloon-like expansion of the vessel that grows over years. If abdominal aortic aneurysms grow large enough, they may burst.
ACID REFLUX OR HEARTBURN
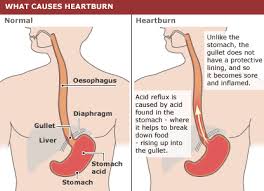
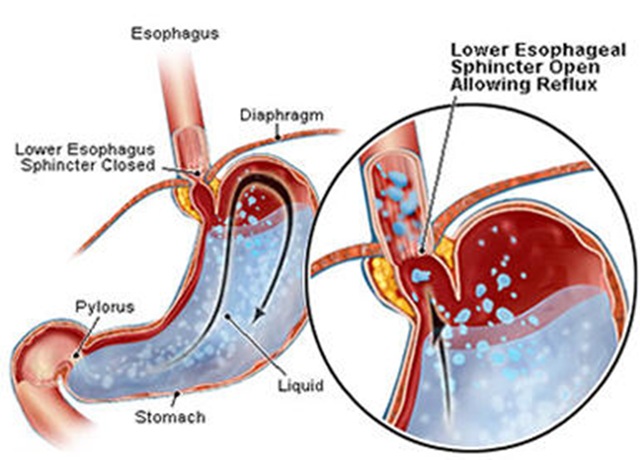
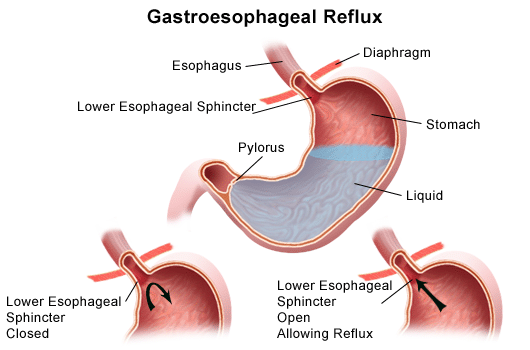
Acid reflux is a condition where there is back flow of gastric acid from the stomach to oesophagus. The oesophageal sphincter lies at the junction where the stomach and the oesophagus join. Normally, the sphincter opens when you swallow, allowing food into your stomach. The rest of the time, it squeezes tight to prevent food and acid in the stomach into the oesophagus. As a result of malfunction of sphincter reflux occurs.
SYMPTOMS
Chest pain behind the breastbone is felt. Heartburn gets worse when you eat, bend or lie down. Tightness in your chest or upper abdomen is felt. Wake you up at night. Regurgitation, the backflow of stomach fluids into your mouth. Nausea, Sore throat, Difficulty Swallowing. A recurring sour or bitter taste in the mouth. Hoarseness, especially in the morning. Coughing, wheezing or repeatedly needing to clear your throat.
CAUSES
Certain food, Pregnancy, Smoking, Alcohol, Pregnancy, Medication, Increased abdominal pressure, because of obesity or pregnancy, A bulge in the stomach (hiatus hernia) that protrudes above the diaphragm.
COLIC & FLATULENCE

Eating is one of the foremost requirements and at the same time pleasures of life. After eating if you do not feel well, it is a clear sign of a medical disorder. Bloated abdomen refers to a feeling of fullness, tightness and distension of abdomen. There is also an excessive accumulation of gas in abdomen. Bloated abdomen can be painful, with cramping as well.
SYMPTOMS
Hiccups and shortness of breath.
THE MAIN CAUSES BEHIND BLOATED ABDOMEN ARE:
Irritable Bowel Syndrome,
Overeating, Constipation, Acid reflux (Dyspepsia),
Taking flatulent (gas-forming) food,
Food intolerance like lactose intolerance,
CONSTIPATION

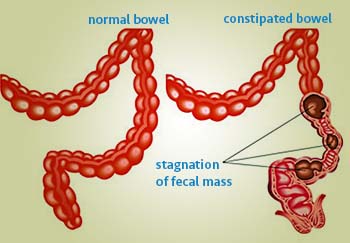

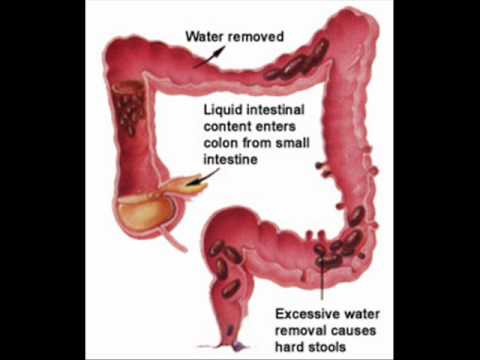
Colon plays an important role in digestion process and stool formation. Digestion process starts as soon as food reaches the stomach. Food is digested so that it can be broken minutely to absorb the nutrients at various stages. As a result when all the nutrients are absorbed the rest of the product is declared waste and forms STOOLS. Muscle contractions of the colon push the stool toward the rectum. By the time stool reaches the rectum it becomes solid, because most of the water has been absorbed. This is expelled via rectum through anus. This is a normal process. As eating is vital to body, expulsion of stools is also important.
Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. It essentially refers to an infrequent bowel movement or difficulty in passing stool. Infrequent bowel movement means passing less than three stools a week. Other indicative symptoms are hard stool, insufficient stool, unsatisfactory stool or a feeling of incomplete bowel evacuation, straining at stool and in extreme cases, a need to use fingers to remove stool. Constipation is a common but painful condition that occurs when bowel movements become infrequent or difficult.
CAUSES
A DIET LOW IN FIBRE
SEDENTARY LIFESTYLE
DECREASED PHYSICAL ACTIVITY & LIQUID INTAKE
CONSUMING CALCIUM OR IRON SUPPLEMENTS
OVERUSE OF MEDICINES SUCH AS ANTI DEPRESSENTS AND LAXATIVES
MEDICAL CONDITIONS LINKED ARE DIABETES, SPINAL CORD LEISIONS,
HYPOTHYROIDISM AND IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME
PREVENTION
Healthy Diet, Exercise, Drink Plenty of Water
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PROBLEMS
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) GASTRIC REFLUXS)
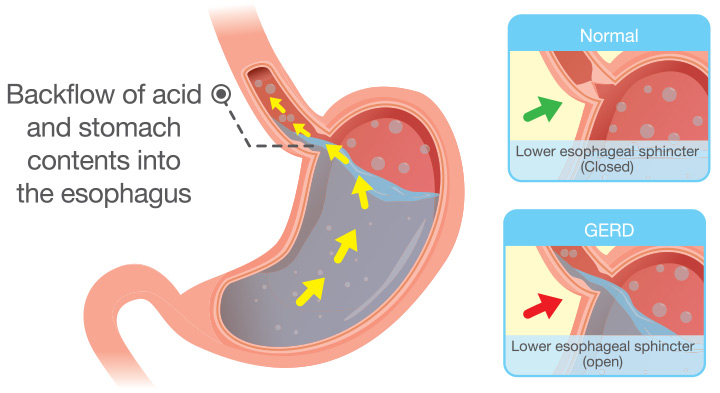
Acid reflux happens when stomach acid backs up into the oesophagus. When this happens, a burning pain in the middle of the chest is felt. It often occurs after meals or at night.
It is common for people to experience acid reflux and heartburn once in a while, If it occurs at least twice each week, it could be a sign of GERD.
The symptoms include persistent heartburn, bad breath, tooth erosion, nausea, pain in chest or upper part of the abdomen or trouble swallowing or breathing.
GALL BLADDER
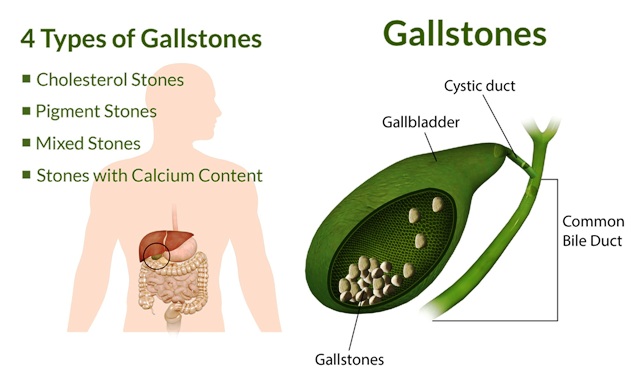
Gallstones are hard deposits that form in your gallbladder. The function of the gall bladder is to secrete bile for digestion and stores. Gallstones can form when there is too much cholesterol or waste in the bile or if the gallbladder does not empty properly. When gallstones block the ducts leading from your gallbladder to your intestines, they can cause sharp pain in your upper-right abdomen.
CELIAC DISEASE
Celiac disease is a serious sensitivity to gluten, which is a protein found in wheat, rye and barley. The immune system attacks and damages the villi when gluten is present. Symptoms of celiac disease in children include abdominal pain and bloating, diarrhoea, constipation, vomiting and weight loss. Symptoms in adults can also include anaemia, fatigue, bone loss, depression, and seizures.
CROHN’S DISEASE
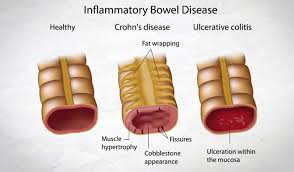
It part of a group of digestive conditions called inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It most commonly affects the terminal ileum, but it can affect any part of the digestive tract. Doctors aren't sure what causes the disease, but it is thought that genetics and family history may play a part. The most common symptoms are abdominal pain, diarrhoea, rectal bleeding, weight loss and fever.
ULCERATIVE COLITIS
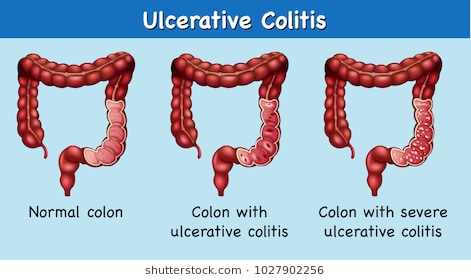
It is another inflammatory bowel disease. The symptoms of ulcerative colitis are very similar to those of Crohn's but the part of the digestive tract affected is solely the large intestine. The immune system mistakes food or other materials for invaders, sores or ulcers develop in the lining of the colon. The symptoms are frequent and urgent bowel movements, pain and diarrhoea; stool contains blood or abdominal cramps. In severe cases, treatment for ulcerative colitis may involve surgery to remove the colon.
IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME
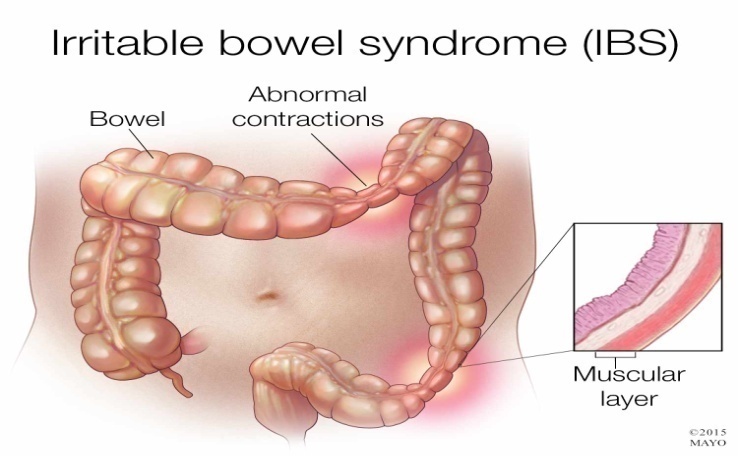
IBS is another common digestive condition. The symptoms are constipation, bloating, diarrhoea, or hard, dry stools on one day and loose watery stools on another.
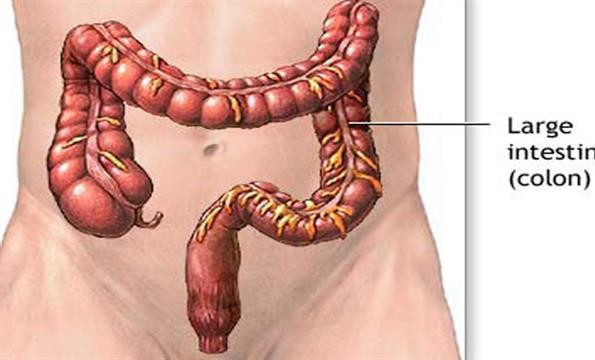
DIVERTICULITIS

Small pouches called diverticula form in weak spots of the digestive system especially the colon. If you have diverticula but no symptoms, the condition is called diverticulosis, which is quite common among older adults and rarely causes problems. But if the pouches become inflamed, it’s called diverticulitis. Symptoms include fever and abdominal pain. Obesity is a major risk factor for diverticulitis.
HEMORRHOIDS
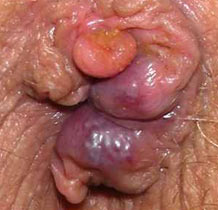
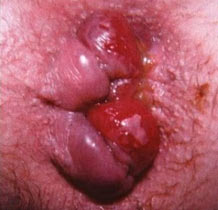
Bright red blood in the toilet bowl could be a sign of of haemorrhoids. It is an inflammation of the blood vessels at the end of your digestive tract. They can be painful and itchy. The causes include chronic constipation, diarrhoea, straining during bowel movements and a lack of fibre in the diet.
ANAL FISSURE
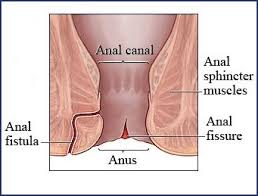
Anal fissures are tiny, oval-shaped tears in the lining of anus. The symptoms are similar to those of haemorrhoids. Bleeding and pain are common. Straining and hard bowel movements can cause fissures, so can soft stools and diarrhoea.
HELICOBACTER PYLORI
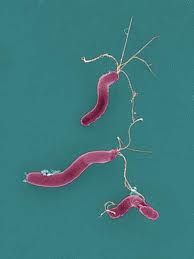
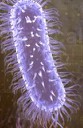
Helicobacter pylori, a type of bacteria that can infect the stomach or duodenum (first part of the small intestine). If left untreated, H. pylori bacteria can cause gastritis (an inflammation or irritation of the stomach lining) and duodenal or gastric ulcers. In addition, infection with H. pylori increases the risk of other diseases and is also a risk factor for gastric cancer. Accurate detection of H. pylori is the first step toward curing stomach and intestinal ulcers and preventing the development of more serious gastrointestinal problems It is one of the most common causes of peptic ulcers and is known to be very obstinate to respond to the treatment. Most people with H. pylori will never have any signs or symptoms, since we may have an innate resistance to its harmful effects.

Helicobacter pylori, a type of bacteria that can infect the stomach or duodenum (first part of the small intestine). If left untreated, H. pylori bacteria can cause gastritis (an inflammation or irritation of the stomach lining) and duodenal or gastric ulcers. In addition, infection with H. pylori increases the risk of other diseases and is also a risk factor for gastric cancer. Accurate detection of H. pylori is the first step toward curing stomach and intestinal ulcers and preventing the development of more serious gastrointestinal problems It is one of the most common causes of peptic ulcers and is known to be very obstinate to respond to the treatment. Most people with H. pylori will never have any signs or symptoms, since we may have an innate resistance to its harmful effects.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
Severe and persistent abdominal pain. Nausea and vomiting
Fullness or bloating of the abdomen. Frequent Burping
Burning in the oesophagus and stomach. Gastritis. Bad Breath. Anaemia.
Dark coloured vomit or black tarry stools.
In severe case, difficulty in swallowing
Chest pain & pain between the shoulder blades
COMPLICATIONS
Ulcers in the stomach wall.
Inflammation of the stomach lining (gastritis).
Severe mal-absorption leading to weight loss.
TESTS FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI
Urea Breath Test.
Blood Test, Stool Test, Biopsy.
Dato' N.Subra Homeopathy
The Homeopathy